保幼激素III,≥65%,JH-III,烟草天蛾激素,CAS号24198-95-6,50mg
价格:12530元
产品说明:
保幼激素III,≥65%
别名:C16-保幼激素, JH-III, 反,反-10,11-环氧-3,7,11-三甲基-2,6-十二碳二烯酸甲酯, 烟草天蛾激素
分子式:C16H26O3
CAS号:24198-95-6
分子量:266.38
结构式:
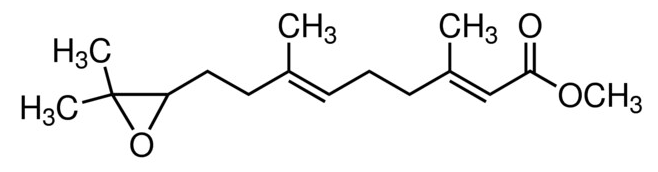
Beilstein:1316317
MDL编号:MFCD00135990
PubChem化学物质编号:24896191
参考文献
1.目录飞蝗细胞色素P450 15A1基因在保幼激素合成中的功能研究
[硕士论文]原少航资源利用与植物保护山西大学2022
摘要:分子质量267.19,这些结果表明LmCYP15A1对MF的代谢产物是JH III。然而高效液相色谱分析LmCYP15A1对FA的代谢产物并没有出现JHA标准品(5.42min)的峰,由此可以判定LmCYP15A1不能将FA代谢为JHA。 综上所述,飞蝗LmCYP15A1在参与保幼激素合成时,FA先经过甲基转移酶的甲基化作用生成了MF,其次MF再经过LmCYP15A1作用生成保幼激素,为直翅目昆虫
直翅目害虫细胞色素P45015家族催化特性保幼激素
下载:21
2.目录飞蝗lncRNA的鉴定及其在卵子发生中的功能
[硕士论文]樊玉宁生物化学与分子生物学河南大学2019
摘要:飞蝗(Locusta migratoria)是一种世界范围的重要农业害虫,具有产卵量大,迁徙能力强的特点,蝗灾的暴发对农业生产造成了巨大的损失。飞蝗的生殖主要由保幼激素(juvenile hormone, JH)调控,JH促进卵黄原蛋白在脂肪体中合成,释放到血淋巴,通过卵泡上皮细胞间的通道(patency)和受体介导的内吞,被正在发育的卵巢吸收,促进卵巢的发育。我们的前期研究表明JH可以通过诱导
飞蝗lncRNA保幼激素卵黄生成,卵形成
被引:2下载:26
3.目录桔小实蝇保幼激素信号通路Met和Kr-h1基因功能初探
[硕士论文]李亚丽农业昆虫与害虫防治西南大学2016
摘要:之下,幼虫孵化后取食果肉,造成果实脱落或失去经济价值。变态发育作为桔小实蝇重要的生理过程,具有重要的研究意义。在昆虫中,蜕皮激素和保幼激素协同作用,共同参与调控昆虫的蜕皮和变态发育。相对于蜕皮激素信号通路,保幼激素(Juvenile hormone,JH)分子作用机制还远未清楚。 本学位论文基于桔小实蝇基因组及转录组数据库信息,运用RT-PCR技术,从桔小实蝇体内克隆获得了JH信号通路基因Met和
桔小实蝇保幼激素信号通路Kr-h1基因变态发育序列分析
被引:5下载:128
4.目录保幼激素调控家蚕寿命的分子机制研究
[硕士论文]李知泉特种经济动物饲养西南大学2016
摘要:旨在探究保幼激素对家蚕寿命的调控。获得的主要研究结果和结论如下: 1.保幼激素含量对家蚕寿命的影响 前人的大量研究表明,用保幼激素类似物处理家蚕幼虫,能够显著延长幼虫的龄期经过。但关于JH对家蚕蛾期的影响尚未见报道。本研究中,我们通过给新羽化蚕蛾注射保幼激素III(juvenile hormone III,JH III)或其类似物甲氧普林(methoprene)发现,雄蛾的寿命均显著缩短,而对雌
家蚕保幼激素BmFoxO基因蚕蛾寿命分子机制
被引:5下载:219
5.目录三疣梭子蟹甲基法尼酯合成及在卵巢发育和蜕皮中的作用
[博士论文]谢熙渔业资源宁波大学2016
摘要:萜类激素甲基法尼酯(MF)是昆虫保幼激素III(JH III)的非环氧化形式,其参与调控甲壳动物的生长、蜕皮、生殖及渗透压调节等多种生理过程,被一致认为是甲壳动物中JH的对等物。MF的生理功能及作用机理一直是甲壳动物内分泌研究的热点,但其在甲壳动物卵巢发育及蜕皮中的作用却存在争议,很有可能因物种的不同而有所区别。由此,本研究对三疣梭子蟹(Portunus trituberculatus)MF合成
三疣梭子蟹卵巢发育转甲基酶基因表达萜类激素甲基法尼酯
被引:2下载:77
6.目录蝶蛹金小蜂毒液分子特性及其调控寄主分子机理的研究
[博士论文]朱家颖环境生物学浙江大学2009
摘要:h内的变化。结果显示,寄生或注射毒液寄主蛹血淋巴的保幼激素(仅检测到III型)滴度在24-72h内显著高于对照组,且在处理12h后保幼激素滴度激急上升;保幼激素酯酶活性在未寄生或注射PBS的蛹血淋巴中分别于6-48h和12-36h显著高于处理组,且其活性分别在12h和24h达到最大值;与处理组相比,蜕皮激素滴度在未寄生或注射PBS的蛹血淋巴中,12-36h之间快速上升,在36h达到峰值,然后下降,
蝶蛹金小蜂毒液分子机理调控寄主
被引:6下载:268
7.包含氰基亚砜亚胺化合物和乙基多杀菌素的杀虫混合物
[专利]发明专利CN200980133379.0巴斯夫欧洲公司申请日:2009-08-24 公开日:2011-07-27
摘要:本发明涉及杀虫混合物,其以协同增效有效量包含如下组分作为活性化合物:1)至少一种式I的氰基亚砜亚胺化合物I,其中X为Cl或CF3;2)乙基多杀菌素;任选地,3)一种选自包括乙酰胆碱酯酶抑制剂、GABA门控氯离子通道拮抗剂、钠通道调节剂、烟碱乙酰胆碱受体激动剂/拮抗剂、氯离子通道活化剂、保幼激素类似物、影响氧化磷酸化的化合物
相关信息:
一般描述
研究领域:细胞信号传导
保幼激素III (JH III)是昆虫体内最普遍的保幼激素 (JH)。[1]
应用
保幼激素 III 已用于:
保幼激素对褶皱臂尾轮虫混交雌体的产生的影响[2]
研究保幼激素对成年蜜蜂头部 GB19811(假定的Takeout/保幼激素结合蛋白)mRNA 水平的影响[3]
研究保幼激素对地熊蜂促促性腺和生理功能的影响[4]
生化/生理作用
JHBP(JH 结合蛋白)可保护JH(保幼激素)免受JH酯酶和环氧化物水解酶介导降解。它们还有助于将JH传递到靶组织。[5]保幼激素(JHs) 是一组无环倍半萜类化合物,在某些昆虫谱系中,这些化合物的法尼醇骨架经过化学修饰,产生一系列同源激素。JH是昆虫发育和繁殖全方位必需的成分。它在社会性昆虫的变态和等级决定中具有关键作用。它可调节行为、多形性、幼虫和成虫滞育以及卵巢发育。[1]保幼激素 III (JH III) 的倍半萜类骨架是通过蟑螂的经典甲羟戊酸(MVA)途径生物合成的。[6]
控制昆虫的幼虫变态,包括保留幼体特征。
参考文献
Protein kinase C modulates transcriptional activation by the juvenile hormone receptor methoprene-tolerant.
Reyhaneh Ojani et al.
Insect biochemistry and molecular biology, 70, 44-52 (2015-12-23)
Juvenile hormone (JH) controls many biological events in insects by triggering dramatic changes in gene expression in target cells. The Methoprene-tolerant (MET) protein, an intracellular JH receptor, acts as a transcriptional regulator and binds to the promoters of tissue- and
Juvenile hormone affects the splicing of Culex quinquefasciatus early trypsin messenger RNA.
Dov Borovsky et al.
Archives of insect biochemistry and physiology, 99(3), e21506-e21506 (2018-09-04)
The full length of Culex quiquefasciatus early trypsin has been cloned and sequenced and a three-dimensional (3D) model of the enzyme was built showing that the enzyme has the canonical trypsin's active pocket containing H78, D123, S129, and D128. The Regulation of Gene Expression Patterns in Mosquito Reproduction.
Sourav Roy et al.
PLoS genetics, 11(8), e1005450-e1005450 (2015-08-15)
In multicellular organisms, development, growth and reproduction require coordinated expression of numerous functional and regulatory genes. Insects, in addition to being the most speciose animal group with enormous biological and economical significance, represent outstanding model organisms for studying regulation of
Juvenile hormone levels are increased in winners of cockroach fights.
Rong Kou et al.
Hormones and behavior, 54(4), 521-527 (2008-07-29)
In lobster cockroach (Nauphoeta cinerea) adult males, concomitant expression of attack behavior and an increase in juvenile hormone (JH) III titer can be induced by contact with an isolated antenna [Chou et al., 2007. Antenna contact and agonism in the
Juvenile hormone regulates brain-reproduction tradeoff in bumble bees but not in honey bees.
Hagai Y Shpigler et al.
Hormones and behavior, 126, 104844-104844 (2020-08-30)
Gonadotropic hormones coordinate processes in diverse tissues regulating animal reproductive physiology and behavior. Juvenile hormone (JH) is the ancient and most common gonadotropin in insects, but not in advanced eusocial honey bees and some ants. To start probing the evolutionary
Microarray analysis of juvenile hormone response in Drosophila melanogaster S2 cells.
David K Willis et al.
Journal of insect science (Online), 10, 66-66 (2010-08-03)
A microchip array encompassing probes for 14,010 genes of Drosophila melanogaster was used to analyze the effect of juvenile hormone (JH) on genome-wide gene expression. JH is a member of a group of insect hormones involved in regulating larval development
Biological activities of juvenile hormone III skipped bisepoxide in last instar nymphs and adults of a stink bug, Plautia stali.
Toyomi Kotaki et al.
Journal of insect physiology, 57(1), 147-152 (2010-10-26)
Juvenile hormone III skipped bisepoxide (JHSB(3)), methyl (2R,3S,10R)-2,3;10,11-bisepoxyfarnesoate was recently determined as a novel juvenile hormone (JH) in a stink bug, Plautia stali. To further confirm the biological function of JHSB(3) in this insect, its juvenilizing, reproduction-stimulating and diapause-terminating activities
Pheromone, juvenile hormone, and social status in the male lobster cockroach Nauphoeta cinerea.
Rong Kou et al.
Archives of insect biochemistry and physiology, 68(3), 144-155 (2008-05-06)
In this study, the major pheromone component, 3-hydroxy-2-butanone (3H-2B), released by dominants was measured during early scotophase. Both the JH III titer in the hemolymph and the 3H-2B content of the sternal glands of the dominants and subordinates were then
Involvement of the transcription factor E75 in adult cuticular formation in the red flour beetle Tribolium castaneum.
Gelyn D Sapin et al.
Insect biochemistry and molecular biology, 126, 103450-103450 (2020-08-21)
Insect adult metamorphosis generally proceeds with undetectable levels of juvenile hormone (JH). In adult development of the red flour beetle Tribolium castaneum, biosynthesis of adult cuticle followed by its pigmentation and sclerotization occurs, and dark coloration of the cuticle becomes
Orcokinins contribute to the regulation of vitellogenin transcription in the cockroach Blattella germanica.
Sheila Ons et al.
Journal of insect physiology, 82, 129-133 (2015-10-16)
Orcokinins (OKs) are neuropeptides that were first identified in crustacean through their myotropic activity. In insects, the OK gene gives rise to two mRNAs coding for two different families of conserved mature neuropeptides: OKA and OKB. Although OKs are conserved
Insulin-like peptide DILP6 regulates juvenile hormone and dopamine metabolism in Drosophila females.
I Yu Rauschenbach et al.
General and comparative endocrinology, 243, 1-9 (2016-11-09)
Insulin-like peptide DILP6 is a component of the insulin/insulin-like growth factor signalling pathway of Drosophila. Juvenile hormone (JH) and dopamine (DA) are involved in the stress response and in the control of reproduction. In this study, we investigate whether DILP6
The Broad Complex isoform 2 (BrC-Z2) transcriptional factor plays a critical role in vitellogenin transcription in the silkworm Bombyx mori.
Congwen Yang et al.
Biochimica et biophysica acta, 1840(9), 2674-2684 (2014-05-28)
Vitellogenin (Vg) is synthesized in the fat body of the female silkworm Bombyx mori and transported to the oocyte as a source of nutrition for embryo development. It is well known that ecdysone regulates physiological, developmental and behavioral events in
Genetic Evidence for Function of the bHLH-PAS Protein Gce/Met As a Juvenile Hormone Receptor.
Marek Jindra et al.
PLoS genetics, 11(7), e1005394-e1005394 (2015-07-15)
Juvenile hormones (JHs) play a major role in controlling development and reproduction in insects and other arthropods. Synthetic JH-mimicking compounds such as methoprene are employed as potent insecticides against significant agricultural, household and disease vector pests. However, a receptor mediating
Juvenile hormone regulation of Drosophila Epac–a guanine nucleotide exchange factor.
Jun Wang et al.
Molecular and cellular endocrinology, 305(1-2), 30-37 (2009-05-13)
Real-time quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) was used to characterize the effects of juvenile hormone (JH) on Epac (Exchange Protein directly Activated by Cyclic AMP; NM_001103732), a guanine nucleotide exchange factor for Rap1 in Drosophila S2 cells. JH
Knockout silkworms reveal a dispensable role for juvenile hormones in holometabolous life cycle.
Takaaki Daimon et al.
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 112(31), E4226-E4235 (2015-07-22)
Insect juvenile hormones (JHs) prevent precocious metamorphosis and allow larvae to undergo multiple rounds of status quo molts. However, the roles of JHs during the embryonic and very early larval stages have not been fully understood. We generated and characterized
Winner and loser effects in lobster cockroach contests for social dominance.
Rong Kou et al.
Hormones and behavior, 107, 49-60 (2018-12-12)
In the context of animal aggression, the winner/loser effect is a cross-taxa phenomenon. In the present study, the effect of social contest experience on winning and losing subsequent encounters was investigated in the furious male lobster cockroach, Nauphoeta cinerea. Dominant
Quorum Sensing Activity and Hyphal Growth by External Stimuli in the Entomopathogenic Fungus Ophiocordyceps sinensis.
Guiqing Liu et al.
Insects, 11(4) (2020-04-01)
The entomopathogenic fungus Ophiocordyceps sinensis is one of the best known and most precious medicines and health food in China. The blastospores-hyphae (dimorphism) transition of this fungus in host hemolymph is critical for the virulence and the mummification of host
Liquid chromatography coupled to ion trap-tandem mass spectrometry to evaluate juvenile hormone III levels in bee hemolymph from Nosema spp. infected colonies.
A M Ares et al.
Journal of chromatography. B, Analytical technologies in the biomedical and life sciences, 899, 146-153 (2012-06-06)
It has been described a fast, simple and sensitive liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) method to measure juvenile hormone III (JH III), which was used to study of the effects of Nosema spp. infection on JH III levels in bee
Common structural features facilitate the simultaneous identification and quantification of the five most common juvenile hormones by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry.
Cesar E Ramirez et al.
Insect biochemistry and molecular biology, 116, 103287-103287 (2019-11-25)
This study reports the development and application of a liquid chromatography method coupled to electrospray tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) for the identification and quantification of the five most common juvenile hormone (JH) homologs and methyl farnesoate (MF). The protocol allows
Ontogeny of pioneer neurons in the antennal nervous system of the grasshopper Schistocerca gregaria.
George Boyan et al.
Development genes and evolution, 227(1), 11-23 (2016-11-12)
The nervous system of the antenna of the grasshopper Schistocerca gregaria consists of two nerve tracts in which sensory cells project their axons to the brain. Each tract is pioneered early in embryogenesis by a pair of identified cells located
Socio-environmental and endocrine influences on developmental and caste-regulatory gene expression in the eusocial termite Reticulitermes flavipes.
Matthew R Tarver et al.
BMC molecular biology, 11, 28-28 (2010-04-27)
Strict regulation of caste differentiation, at the molecular level, is thought to be important to maintain social structure in insect societies. Previously, a number of extrinsic and intrinsic factors have been shown to influence caste composition in termite colonies. One
The environmental-endocrine basis of gynandromorphism (intersex) in a crustacean.
Allen W Olmstead et al.
International journal of biological sciences, 3(2), 77-84 (2007-01-06)
Commensurate with the decline in many crustacean populations has been an accumulation in reports of sexually ambiguous individuals within these populations. The cause of gynandromorphism or intersex among crustaceans is unknown. We show that gynandromorphism in the branchiopod crustacean Daphnia
Structural and RNAi characterization of the German cockroach lipophorin receptor, and the evolutionary relationships of lipoprotein receptors.
Laura Ciudad et al.
BMC molecular biology, 8, 53-53 (2007-06-26)
Lipophorin receptors (LpRs) have been described in a number of insects, but functional studies have been reported only in locusts and mosquitoes. The aim of the present work was to characterize the LpR of the cockroach Blattella germanica, not only
NADP+-dependent farnesol dehydrogenase, a corpora allata enzyme involved in juvenile hormone synthesis.
Jaime G Mayoral et al.
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 106(50), 21091-21096 (2009-11-27)
The synthesis of juvenile hormone (JH) is an attractive target for control of insect pests and vectors of disease, but the minute size of the corpora allata (CA), the glands that synthesize JH, has made it difficult to identify important
Juvenile hormone controls ovarian development in female Anopheles albimanus mosquitoes.
Salvador Hernández-Martínez et al.
Scientific reports, 9(1), 2127-2127 (2019-02-16)
Anophelinae mosquitoes are vectors of human malaria, a disease that infects hundreds of millions of people and causes almost 600,000 fatalities annually. Despite their medical importance, laboratory studies on key aspects of Anophelinae reproductive biology have been limited, and in
Differential impacts of juvenile hormone, soldier head extract and alternate caste phenotypes on host and symbiont transcriptome composition in the gut of the termite Reticulitermes flavipes.
Ruchira Sen et al.
BMC genomics, 14, 491-491 (2013-07-23)
Termites are highly eusocial insects and show a division of labor whereby morphologically distinct individuals specialize in distinct tasks. In the lower termite Reticulitermes flavipes (Rhinotermitidae), non-reproducing individuals form the worker and soldier castes, which specialize in helping (e.g., brood
Cloning and expressing a highly functional and substrate specific farnesoic acid o-methyltransferase from the Asian citrus psyllid (Diaphorina citri Kuwayama).
Evelien Van Ekert et al.
FEBS open bio, 5, 264-275 (2015-04-22)
The Asian citrus psyllid, Diaphorina citri, transmits a phloem-limited bacterium, Candidatus 'Liberibacter' asiaticus that causes citrus greening disease. Because juvenile hormone (JH) plays an important role in adult and nymphal development, we studied the final steps in JH biosynthesis in
Reduced fecundity and regulation of reproductive factors in flubendiamide-resistant strains of Plutella xylostella.
Shi-Qing Sun et al.
Pesticide biochemistry and physiology, 169, 104668-104668 (2020-08-24)
Diamondback moth (DBM), Plutella xylostella, is an important pest of crucifers worldwide. The extensive use of flubendiamide has led to the development of resistance in field populations and reports of control failures. In this study, the lab-selected (Rf) and field-collected
Frizzled 2 Functions in the Regulation of TOR-Mediated Embryonic Development and Fecundity in Cyrtorhinus lividipennis Reuter.
Linquan Ge et al.
Frontiers in physiology, 11, 579233-579233 (2020-10-13)
The mirid bug, Cyrtorhinus lividipennis Reuter, is an important predator of rice planthoppers in Asia. In a previous study, C. lividipennis fed on gramineous weeds with brown planthopper (BPH) eggs had reduced development compared to those fed on rice with
Sexual difference in juvenile-hormone titer in workers leads to sex-biased soldier differentiation in termites.
Kouhei Toga et al.
Journal of insect physiology, 87, 63-70 (2016-02-13)
In termites, the soldier caste, with its specialized defensive morphology, is one of the most important characteristics for sociality. Most of the basal termite species have both male and female soldiers, and the soldier sex ratio is almost equal or
关键词:生化试剂,活性分子,抑制剂
原网址;https://www.sima-lab.com/pro_53756713.html

